Cataract
What are Cataracts?
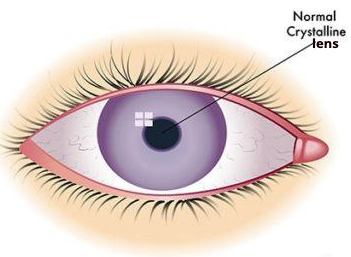
Cataracts are cloudiness of the lens inside the eye and are one of the most common eye conditions.
As patients mature, the clear lens inside the eye begins to become cloudy and can also harden. As the lens becomes increasingly cloudy the vision out of the affected eye is reduced.
Patients often complain of a "film" across their vision, or "cloudy vision". Others refer to blurry vision or glare.
Patients are often apprehensive that they may go blind. This, of course, is rarely going to happen. Cataract surgery is very common and highly successful operation to restore clear vision. Cataract surgery is performed as a day-only procedure in a hospital. The procedure is comfortable and well tolerated.
A Cataract is not...
A cataract is not a tumour, nor is it a "film" or tissue growth that develops over the cornea, or front surface of the eye.
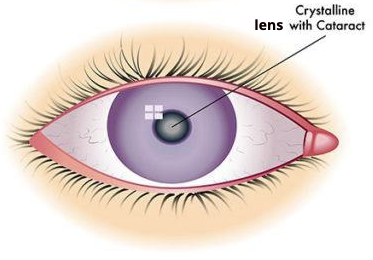
The majority of cataracts are not visible to the naked eye although in some instances the pupil can appear white because the lens is completely clouded by a very dense cataract.
Who is at risk of Cataracts?
Often, patients are in their 70’s or 80’s when cataracts become a problem. The development of a cataract can occur as:
- A part of the natural ageing process,
- An inherited attribute,
- A complication of other diseases such as diabetes.
Patients are also at increased risk of cataract formation as a result of:
- prolonged use of corticosteroids
- excessive exposure to UV rays (sunlight)
- exposure to X-rays and other radiation during radiotherapy
- injury or trauma
Younger patients, who may have had an injury to the eye, can also be affected at a much earlier age.
What Causes Cataracts?
Any structural change in the lens proteins can alter its clarity and negatively impact vision.
The eye’s lens is located behind the iris (the coloured portion of the eye), and it is mostly made up of water and proteins. These specific proteins provide the lens with its transparent structure.
When a cataract occurs, the lens becomes cloudy and is seen as opacification in the lens sitting behind the pupil, when viewed through a microscope.
With time, the lens becomes more cloudy and when very dense can be seen as white haze in the pupil.
What Are the Symptoms of Cataracts?
Symptoms commonly associated with Cataracts include:
- Blurry or cloudy vision
- Faded colours
- Increased or extreme glare from lights
- Poor vision at night
- A difficulty with either near vision or distance vision
- Halos around lights
- Frequent change in eye prescription
What are the Stages of Cataracts?
Initially, only a small part of the eye lens is affected, and you will not notice any vision loss.
Over time, the cataract can grow denser, with your vision becoming increasingly cloudy.
Types of Cataracts
Cataracts may be classified based on their location within the eye, which include:
- Nuclear Cataract - Cloudiness is present in the centre of the lens.
- Cortical Cataract - Cloudiness is seen as white spokes in the outer periphery of the lens.
- Posterior Subcapsular Cataract - This occurs at the back of the lens capsule, which is like a shell of the lens. It may develop quicker than the other types of Cataracts and it is more commonly seen in patients with diabetes or on long-term steroid treatment.
Diagnosis of Cataracts
To assess the impact of the cataract on your vision, your ophthalmologist will perform the following tests:
- Visual Acuity Test - This test involves reading an eye chart from a certain distance with one eye at a time.
- Eye Examination - A comprehensive eye examination will then be performed to assess the severity of the cataract.
- Slit Lamp Examination - A slit lamp examination uses a microscope to examine the structures in front of the eye such as the lens and cornea, which are illuminated by a bright line of light. Using lenses, the retina (at the back of the eye) will also be examined to exclude other causes for a reduction in vision.
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) - This machine uses light reflection to take a picture of the retina in microscopic detail.
- IOL Master - This machine uses light reflection to measure the curvature of the cornea and length of the eye to individualise the strength of artificial lens implant that will be required for your cataract surgery.
- Corneal Topography - This machine uses light reflections to assess the curvature of the cornea in microscopic detail to determine if your eye is suitable for a premium lens implant.
Treatment of Cataracts
Surgery is the only treatment option for Cataracts and would be recommended when the severity of the disease and its impact on the patient's daily activities are material.
Cataract Surgery involves removal of the cloudy lens inside your eye and replacement with an artificial one. The ophthalmologists use the latest technology in advanced phacoemulsification to remove the Cataract under localised anaesthesia. Cataract surgery is performed as a day-only procedure in a hospital. The procedure is comfortable and well tolerated.
What are the Consequences of Untreated Cataracts?
Cataracts do not heal on their own or with conservative treatment. Vision loss will only get worse and could eventually lead to blindness if not treated by surgery.